Which Sterilization Technique Is Best for Your Medical Device?
Sterilization: What is it?
Any procedure that eliminates, destroys, or deactivates all life is called sterilization. The word “sterile,” which denotes the total absence of live germs with the capacity to proliferate, is associated with sterilization. Any bacteria found in items obtained during manufacture are eliminated by sterilization procedures. Sterilized products are frequently thermally or chemically sterilized after being put into their final packaging containers. We’ll go over the various sterilization techniques in this post, including ethylene oxide sterilization techniques, dry heat sterilization techniques, moist heat sterilization techniques, and which sterilization technique is best for the materials in your device based on our comparison chart.
What choices do I have for sterilizing medical devices?
Sterilization of medical devices can be done in seven main ways. Steam sterilization, radiation sterilization, dry heat sterilization, filtration sterilization, gas sterilization (including ethylene oxide sterilization), vapor sterilization, and liquid sterilization are some of these techniques. Gas sterilization, vapor sterilization, and liquid sterilization are chemical sterilization processes among these technologies. Steam and dry heat sterilization are thermal sterilization methods, as you might anticipate. Each sterilizing method is briefly described in Table 1 below.

Table 1: Descriptions of Sterilization Methods
What is the best way to sterilize your medical device?
The materials your medical gadget is composed of will largely determine which sterilization method is best for it. The biological component of almost all devices containing biologics needs to be sterilized via filtration. Steam sterilization is the most often used and least expensive sterilization technique. Autoclaves will be used to disinfect devices composed of metal or other materials that can be sanitized by steam. Ethylene oxide gas sterilization is the second most popular sterilizing technique. Heat-sensitive items are frequently sterilized using ethylene oxide gas. But for specific medical device applications, some polymers absorb ethylene oxide (EtO) excessively and have too many hazardous EtO residues. The most efficient “cold” sterilization technique is radiation. Nevertheless, radiation sterilization is more costly, more difficult to outsource, and necessitates the use of materials that degrade when exposed to radiation. For quicker outcomes, vapor phase sterilization is occasionally utilized in place of steam. For medical devices, liquid sterilization is extremely uncommon and frequently never used.
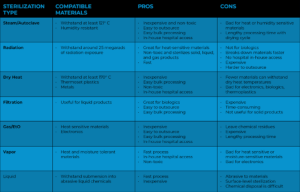
Table 2: Comparison Chart of Medical Device Sterilization Techniques
In Brief
Sterilization refers to any procedure that eliminates, destroys, or deactivates all living things. Sterilization of medical devices can be done in seven main ways. These techniques include gas sterilization (including ethylene oxide sterilization), vapor sterilization, liquid sterilization, dry heat sterilization, radiation sterilization, moist heat sterilization, and sterilization by filtration. The materials your medical gadget is composed of will largely determine which sterilization method is best for it. To determine which kind of sterilization technique is best for your medical device or product, refer to the comparison chart in this page. Additionally, while outsourcing regulatory testing, be sure the company you work with can provide you with the right sterilizing validations for your particular medical device requirements.







